双引擎的基础, vite 在 dev 的插件机制
我们都知道,vite 在开发时使用的是 esbuild 作为依赖预构建和 ts、jsx 文件转译工具,通过浏览器的 ESM 加载,而在生产打包时使用的是 Rollup 作为打包工具。这样的双引擎架构可以同时享受到到开发时 esbuild 的极速体验,也可以在生产打包时使用 Rollup 实现代码分割、自动预加载、异步 chunk 加载优化等,但这同时也带来一个问题:在开发环境,如何兼容 Rollup 的插件?
在 vite 中的解决方案是
- 在开发阶段,借鉴 WMR 思路,实现插件容器机制,模拟 Rollup 调度各个 Vite 插件的执行逻辑
- vite 的插件语法完全兼容 Rollup
下面就具体分析一下 vite 在开发环境的插件机制实现原理
实现原理
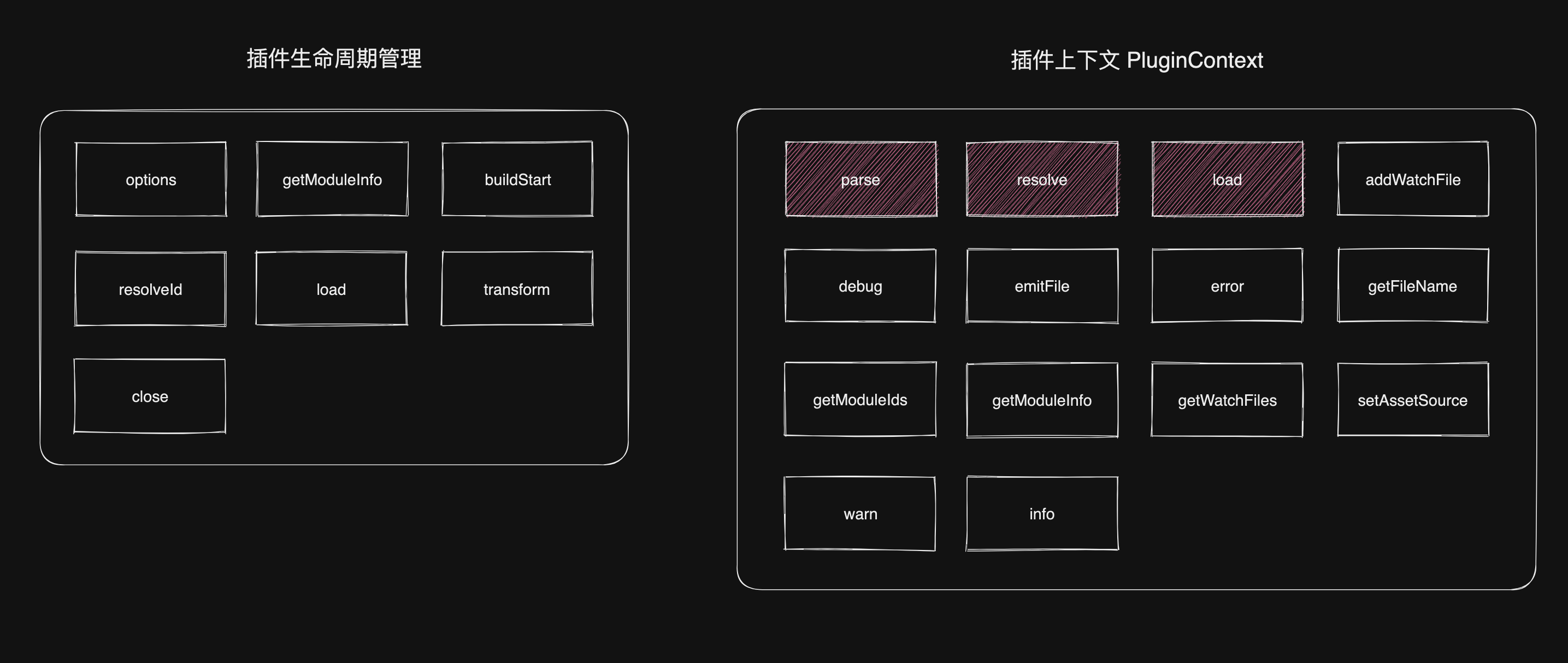
在 vite 启动 server 的过程中,会通过 createPluginContainer 方法创建插件容器,在之前的文章提到过,插件容器主要有三个作用
- 管理的插件的生命周期
- 在插件之间传递上下文对象,上下文对象包含 vite 的内部状态和配置信息,这样插件通过上下文对象就能访问和修改 vite 内部状态
- 根据插件的钩子函数,在特定的时机执行插件
const container = await createPluginContainer(config, moduleGraph, watcher)
其中前两个作用十分重要,下面我们就逐步分析插件容器生命周期管理和传递上下文的实现原理
管理插件生命周期
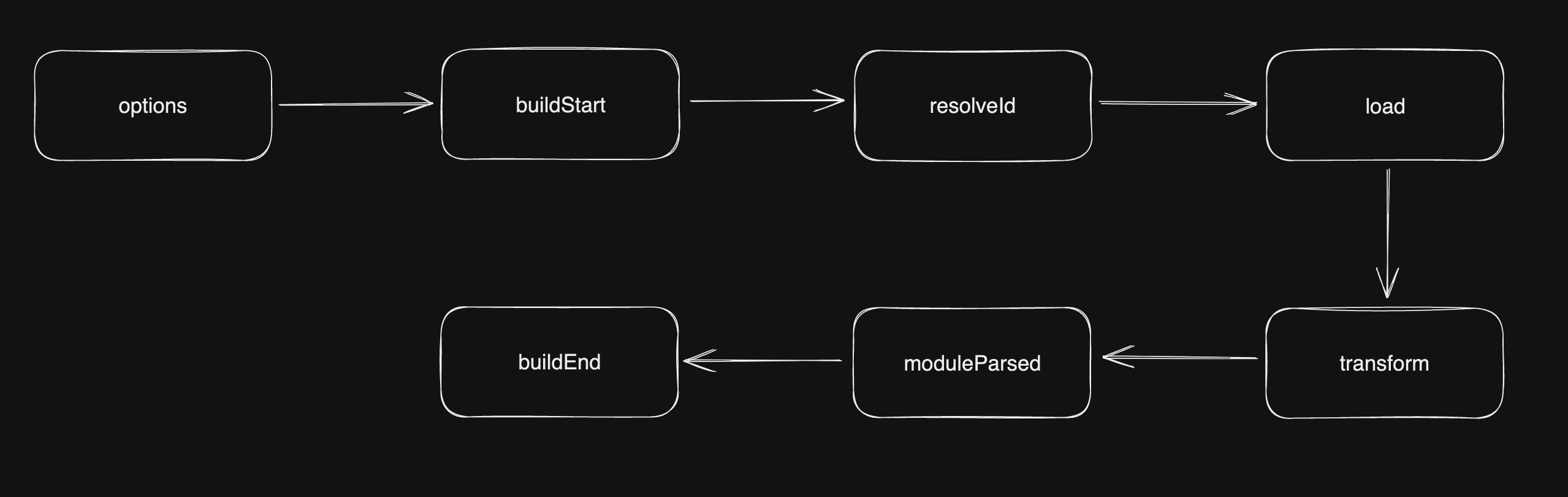
在开发阶段,vite 会模拟 Rollup 的插件执行逻辑,所以先介绍一下 Rollup 的插件执行机制,这里主要介绍 Rollup 的 build 相关钩子
- 调用
options钩子转换配置,得到处理后的配置对象 - 调用
buildStart钩子,开始构建流程 - 调用
resolveId钩子解析文件路径(从input配置指定的入口文件开始) - 调用
load钩子加载模块内容 - 执行所有
transform钩子对模块内容进行自定义转换(比如 babel 转译) - 拿到最后的模块内容,进行 AST 分析,得到所有的 import 内容,调用
moduleParsed钩子 - 所有的 import 都解析完毕,执行
buildEnd钩子,Build 阶段结束
在 vite 中由于 AST 分析是通过 esbuild 进行的,所有没有模拟 moduleParsed 钩子,并且使用 close 钩子封装了 Rollup 的 buildEnd 钩子和 closeBundle 钩子
在 vite 中模拟了如下钩子,下面会详细讲讲每个钩子的实现
options:存储插件容器的配置,用于获取用户传入的配置buildStart:构建开始阶段的钩子函数,执行自定义初始化操作resolveId:解析依赖的钩子函数,对模块依赖进行自定义解析或转换load:加载模块的钩子函数transform:代码转换钩子函数,对代码进行自定义转换或优化close:插件容器关闭阶段钩子函数,执行清理或者收尾工作
// 文件地址:packages/vite/src/node/server/pluginContainer.ts
const container: PluginContainer = {
options,
getModuleInfo,
async buildStart() {},
async resolveId() {},
async load() {},
async transform() {},
async close() {},
}
options 钩子
options 钩子是一个立即执行函数,在插件容器创建的时候,就立即执行 options 方法来获取配置选项
执行过程中会遍历所有 options 钩子,通过 handleHookPromise 方法执行,如果配置中有 acornInjectPlugins 属性的话会注册到 acorn.Parser 解析器中,用于自定义 AST 解析过程
const container: PluginContainer = {
options: await(async () => {
let options = rollupOptions
// 遍历所有 options 钩子
for (const optionsHook of getSortedPluginHooks('options')) {
options =
(await handleHookPromise(optionsHook.call(minimalContext, options))) ||
options
}
if (options.acornInjectPlugins) {
parser = acorn.Parser.extend(
...(arraify(options.acornInjectPlugins) as any)
)
}
return {
acorn,
acornInjectPlugins: [],
...options,
}
})(),
}
钩子函数统一都会通过 handleHookPromise 方法执行,方法会将 promise 函数执行放入 Set 集合中执行,有两个好处
- 可以追踪所有 Promise 的执行过程,close 时可以保证所有异步任务执行完成再关闭
- 可以去处重复的异步任务
const processesing = new Set<Promise<any>>()
function handleHookPromise<T>(maybePromise: undefined | T | Promise<T>) {
// 如果不是 Promise 直接返回
if (!(maybePromise as any)?.then) {
return maybePromise
}
// Promise 异步任务放入集合
const promise = maybePromise as Promise<T>
processesing.add(promise)
// 异步任务执行完成后从集合移除
return promise.finally(() => processesing.delete(promise))
}
getModuleInfo 钩子
getModuleInfo 钩子用于从模块依赖图中获取模块信息,在没有模块信息的时候会通过 Proxy 创建一个代理对象再返回模块信息,使用 Proxy 的好处在于
- 能够限制数据操作权限,只能有 get 获取操作,而不能有其他修改操作
- 动态生成模块信息,可以节约内存,在需要的时候才生成模块信息
const container: PluginContainer = {
getModuleInfo(id: string) {
// 从模块依赖图获取模块,如果没有则返回
const module = moduleGraph?.getModuleById(id)
if (!module) return null
// 如果没有 module.info 模块信息,则通过 Proxy 创建一个代理访问对象
if (!module.info) {
module.info = new Proxy(
{ id, meta: module.meta || EMPTY_OBJECT } as ModuleInfo,
ModuleInfoProxy
)
}
return module.info
},
}
const ModuleInfoProxy: ProxyHandler<ModuleInfo> = {
get(info: any, key: string) {
if (key in info) {
return info[key]
}
},
}
buildStart 钩子
buildStart 钩子用于在构建开始时做自定义的初始化操作,会通过 hookParallel并行执行所有 buildStart 钩子
const container: PluginContainer = {
async buildStart() {
await handleHookPromise(
hookParallel(
'buildStart',
(plugin) => new Context(plugin),
() => [container.options as NormalizedInputOptions]
)
)
},
}
// 并行执行所有 Promise 钩子
async function hookParallel<H extends AsyncPluginHooks & ParallelPluginHooks>(
hookName: H,
context: (plugin: Plugin) => ThisType<FunctionPluginHooks[H]>,
args: (plugin: Plugin) => Parameters<FunctionPluginHooks[H]>
): Promise<void> {
const parallelPromises: Promise<unknown>[] = []
for (const plugin of getSortedPlugins(hookName)) {
const hook = plugin[hookName]
if (!hook) continue
const handler: Function = 'handler' in hook ? hook.handler : hook
// sequential 为 true 表示按顺序执行
if ((hook as { sequential?: boolean }).sequential) {
// 先并行执行之前的异步任务
await Promise.all(parallelPromises)
parallelPromises.length = 0
// 执行当前 sequential 为 true 的异步任务
await handler.apply(context(plugin), args(plugin))
} else {
parallelPromises.push(handler.apply(context(plugin), args(plugin)))
}
}
await Promise.all(parallelPromises)
}
resolveId 钩子
resolveId 钩子会遍历已注册的插件,依次调用 resolveId 钩子,直到解析出第一个非空的 id,最后转化为绝对路径或者外部 url 返回
const container: PluginContainer = {
async resolveId(rawId, importer = join(root, 'index.html'), options) {
// 遍历已注册的插件,依次调用 resolveId 钩子
for (const plugin of getSortedPlugins('resolveId')) {
const handler =
'handler' in plugin.resolveId
? plugin.resolveId.handler
: plugin.resolveId
const result = await handleHookPromise(
handler.call(ctx as any, rawId, importer, {
assertions: options?.assertions ?? {},
custom: options?.custom,
isEntry: !!options?.isEntry,
ssr,
scan,
})
)
if (typeof result === 'string') {
id = result
} else {
id = result.id
Object.assign(partial, result)
}
// 如果找到一个非空的 id,则跳出循环,不再继续调用后续插件的 resolveId 钩子函数
break
}
if (id) {
// 对解析出的 id 进行处理,将其转换为绝对路径或外部 URL
partial.id = isExternalUrl(id) ? id : normalizePath(id)
return partial as PartialResolvedId
} else {
// 没有找到匹配的解析路径,则返回 null
return null
}
},
}
load 钩子
load 钩子用于加载模块时的操作,遍历和执行所有 load 钩子,如果有返回结果的话,更新模块信息
const container: PluginContainer = {
async load(id, options) {
const ctx = new Context()
// 循环遍历 load 插件
for (const plugin of getSortedPlugins('load')) {
const handler =
'handler' in plugin.load ? plugin.load.handler : plugin.load
// 执行 handler.call 方法
const result = await handleHookPromise(
handler.call(ctx as any, id, { ssr })
)
// 如果存在返回结果的话,会更新模块信息
if (result != null) {
if (isObject(result)) {
updateModuleInfo(id, result)
}
return result
}
}
return null
},
}
transform 钩子
transform 钩子用于转换代码的自定义操作,和 load钩子类似,同样是遍历并执行所有 transform 钩子,如果有返回结果的话,更新模块信息
const container: PluginContainer = {
async transform(code, id, options) {
const ctx = new TransformContext(id, code, inMap as SourceMap)
// 遍历 transform 插件
for (const plugin of getSortedPlugins('transform')) {
let result: TransformResult | string | undefined
const handler =
'handler' in plugin.transform
? plugin.transform.handler
: plugin.transform
// 执行插件方法
try {
result = await handleHookPromise(
handler.call(ctx as any, code, id),
)
}
if (!result) continue
// 更新模块信息
updateModuleInfo(id, result)
}
return {
code,
map: ctx._getCombinedSourcemap(),
}
}
}
close 钩子
close 用结束阶段的自定义操作,首先会通过 Promise.allSettled 方法确保异步任务集合里的任务全部执行完成,再依次调用 buildEnd 和 closeBundle 钩子
const container: PluginContainer = {
async close() {
if (closed) return
closed = true
await Promise.allSettled(Array.from(processesing))
const ctx = new Context()
await hookParallel(
'buildEnd',
() => ctx,
() => []
)
await hookParallel(
'closeBundle',
() => ctx,
() => []
)
},
}
传递上下文对象
上下文对象通过 Context 实现 PluginContext 接口定义,PluginContext 实际上是 Rollup 内部定义的类型,可以看到 vite 实现了 Rollup 上下文对象
class Context implements PluginContext {
//... 具体实现
}
type PluginContext = Omit<
RollupPluginContext, // Rollup 定义插件上下文接口
// not documented
| 'cache'
// deprecated
| 'moduleIds'
>
Context 上下文对象一共有 14 个核心方法,其中有 3 个方法是我认为比较核心的方法
- parse:使用 acorn 将代码解析为 AST
- resolve:将相对路径解析为绝对路径,从而正确地处理模块之间的引用
- load:加载特定模块代码
export interface PluginContext extends MinimalPluginContext {
// 将文件添加到 Rollup 的监听列表,文件发生更改时重新编译
addWatchFile: (id: string) => void
// 访问插件缓存,用于在构建之前存储数据(vite 未实现)
cache: PluginCache
// 记录 debug 信息并输出
debug: LoggingFunction
// 允许插件在构建过程中对外暴露生成的文件
emitFile: EmitFile
// 抛出错误并停止构建过程
error: (error: RollupError | string) => never
// 获取资源的文件名
getFileName: (fileReferenceId: string) => string
// 获取当前构建中所有模块的 ID 的迭代器
getModuleIds: () => IterableIterator<string>
// 获取构建中特定模块的信息
getModuleInfo: GetModuleInfo
// 获取 Rollup 在构建过程中监听的文件数组
getWatchFiles: () => string[]
// 将信息记录到 Rollup 构建输出
info: LoggingFunction
// 在构建过程中加载特定模块的代码
load: (
options: { id: string; resolveDependencies?: boolean } & Partial<
PartialNull<ModuleOptions>
>
) => Promise<ModuleInfo>
/** @deprecated Use `this.getModuleIds` instead */
// [已弃用] 提供所有模块 ID 的迭代器(Vite 不实现此方法)
moduleIds: IterableIterator<string>
// 使用 Acorn 解析代码为 AST
parse: (input: string, options?: any) => AcornNode
// 在构建过程中将导入路径解析为绝对文件路径
resolve: (
source: string,
importer?: string,
options?: {
assertions?: Record<string, string>
custom?: CustomPluginOptions
isEntry?: boolean
skipSelf?: boolean
}
) => Promise<ResolvedId | null>
// 设置由其引用 ID 标识的已发出资源的内容
setAssetSource: (
assetReferenceId: string,
source: string | Uint8Array
) => void
// 将警告信息记录到 Rollup 构建输出
warn: LoggingFunction
}
parse 方法比较简单,直接调用了 acorn 的方法将代码解析为 AST
class Context implements PluginContext {
// 调用 acorn.Parser.parse 方法解析代码为 AST
parse(code: string, opts: any = {}) {
return parser.parse(code, {
sourceType: 'module',
ecmaVersion: 'latest',
locations: true,
...opts,
})
}
}
resolve 方法用于将路径解析为绝对路径,具体实现是通过插件容器的 resolveId 方法实现
class Context implements PluginContext {
async resolve( /*...*/ ) {
let out = await container.resolveId(id, importer, {
assertions: options?.assertions,
custom: options?.custom,
isEntry: !!options?.isEntry,
})
if (typeof out === 'string') out = { id: out }
return out as ResolvedId | null
}
// 解析路径具体实现
async resolveId(rawId, importer = join(root, 'index.html'), options) {
},
}
load 方法用于加载指定模块,有四个执行步骤
- 首先执行模块依赖图的
ensureEntryFromUrl方法,确保模块依赖图中存在指定的模块入口 - 其次调用
updateModuleInfo方法更新模块信息 - 然后从指定的入口开始递归加载依赖的模块
- 最后获取加载后的模块信息并返回
class Context implements PluginContext {
async load(
options: {
id: string
resolveDependencies?: boolean
} & Partial<PartialNull<ModuleOptions>>
): Promise<ModuleInfo> {
// 确保模块依赖图中存在指定的模块入口
await moduleGraph?.ensureEntryFromUrl(unwrapId(options.id), this.ssr)
// 更新模块信息的属性
updateModuleInfo(options.id, options)
// 从指定的入口开始递归加载依赖的模块
await container.load(options.id, { ssr: this.ssr })
// 获取加载后的模块信息
const moduleInfo = this.getModuleInfo(options.id)
return moduleInfo
}
}
总结
vite 在 dev 过程中,会使用 createPluginContainer 方法创建插件容器,插件容器有两个核心功能:管理插件生命周期、传递插件上下文
插件生命周期管理主要是模拟 Rollup 的一系列 build 钩子,包括
- options:存储和自定义配置
- getModuleInfo:获取模块信息
- buildStart:构建开始阶段钩子
- resolveId:解析依赖钩子
- load:模块加载钩子
- transform:代码转换钩子
- close:关闭过程清理工作
插件上下文主要用于在插件执行过程中,传递一系列信息,便于插件访问和修改 vite 内部状态,核心操作方法有 14 个,其中有 3 个比较重要
parse方法:将代码解析为 ASTresolve方法:解析路径为绝对路径load方法:加载指定模块